The protein craze hasn’t ended, and for good reason. Protein, one of the three macronutrients essential for good health, is found in every structure in the body, including hair, nails, skin, organs, bones, and muscles. (1) Its benefits, including muscle building, appetite control, metabolism-revving, and bone strengthening, make it a crucial element in maintaining a healthy lifestyle when combined with a balanced diet and regular exercise. (2)
With dizzying protein supplement options on the market today, choosing the best protein powder feels overwhelming. That’s why we’ve tested over 100 of the best protein powders available and compiled 14 of our favorite options to help you narrow down your top contenders. As a registered dietitian nutritionist (RDN), I’ll assess the ingredients and nutrient content to give you a clear understanding of what each product brings to the table.
Editor’s choice: Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate
Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate packs 28 grams of highly effective whey protein isolate into a powder that both tastes great and blends well. Sweetened with stevia, this protein powder is a good low-carb and low-fat option. This top formula is also Informed Choice and Informed Protein certified, meaning it’s independently verified to contain the amount of protein advertised and no banned substances.
Medical disclaimer: This article is intended for educational and informational purposes only. It is not intended as a substitute for medical advice. For health advice, contact a licensed healthcare provider.
Our picks for the best protein powders of 2024
- Best for muscle gain: Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate
- Best for weight loss: Sports Research Whey Protein Isolate
- Best tasting: Legion Whey+
- Best vanilla: Gainful Protein Powder
- Best pea: Nutricost Organic Pea Protein
- Best vegan: Ritual Daily Shake
- Best organic: Ora Organic So Lean & So Clean
- Best low carb: Jacked Factory Authentic Iso
- Best for men: Kaged Protein Isolate Elite
- Best cheap: Cellucor Cor-Performance Whey
- Best unflavored: Promix Whey Protein Powder
- Best for women: Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey
- Best collagen: Momentous Collagen Peptides
- Best chocolate: Dymatize ISO100
How to choose the best protein powder for you
There’s a wide range of protein powders available on the market, and the best protein powder for you can depend on your dietary needs and preferences, as well as your lifestyle.
There are several factors you may want to consider when looking for the best protein powder, including:
Protein type
Whey, casein, soy, pea, and hemp are some of your protein options for protein powder. Choose a powder that provides the best protein type for your goals, needs, and preferences.
For example, if you want to build muscle and have no milk allergies or special dietary needs, you may prefer whey protein, which is considered more anabolic than many other protein sources and may be more effective at supporting muscle growth. (6)
If you follow a vegan or vegetarian diet, you want a plant-based protein powder like pea protein or a plant protein blend.
Food allergies and intolerances may also play a role in your protein choice.
Nutrition facts
Check the nutrition facts label to make sure your protein powder has the right amount of protein. A good protein supplement should provide about 20 grams of protein per serving. (3) Calories count, too. Look for lower-calorie supplements if your goal is weight loss and higher calorie supplements for weight gain.
Flavor and taste
Choose a protein powder that offers your preferred flavors and suits your taste preferences. A good protein powder is one you can easily consume.
Solubility
Solubility, or how well the powder dissolves in liquid, is one of the factors our testers looked at when evaluating a protein powder because it affects quality and customer satisfaction. You want a supplement that’s easy to mix and dissolves well in liquid, otherwise you might have a clumpy or gritty protein shake that’s unpleasant to drink.
Added ingredients
Read the ingredients list and look for protein powders with little to no added sugar or artificial ingredients. Protein powders may also have added active ingredients to support goals like creatine, MCT oil, vitamins, minerals, or other nutrients.
Price
The cost of protein powders varies. Choose one that fits your budget, meets your needs, and tastes good.
Third-party testing
Third-party testing is an independent evaluation of your protein powder that ensures it contains the ingredients listed on the label in the correct amounts. This is an added layer of protection for you that reduces the risk of adverse reactions. Supplements many have a third-party testing seal on the container or mention it on their website.
Compare protein powders

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|

|
|
| Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate | Sports Research Whey Protein Isolate | Legion Whey+ | Gainful Protein Powder | Nutricost Organic Pea Protein | Ritual Daily Shake | Ora Organic So Lean & So Clean | Jacked Factory Authentic Iso | Kaged Protein Isolate Elite | Cellucor Cor-Performance Whey | Promix Unflavored Whey Protein Powder | Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey | Momentous Collagen Peptides | Dymatize ISO100 | |
| Rating | ||||||||||||||
| Servings | 30 | 25 | 30 | 14 | 38 | 15 | 20 | 30 | 24 | 70 | 37 | 22 | 30 | 71 |
| Cost Per Serving | $2.00 | $1.19 | $2.00 | $3.21 | $0.66 | $2.67 | $2.50 | $1.33 | $1.87 | $1–$1.50 | $1.10–$1.42 | $1.55 | $1.73 | $1 |
| Protein Source | Whey Protein Isolate | Whey Protein Isolate | Whey Protein Isolate | Customizable (Whey Protein Isolate or Pea Protein, Brown Rice Protein) | Pea Protein Isolate | Organic Pea Protein | Organic Pea & Rice protein | Whey Protein Isolate | Whey Protein Isolate | Whey Protein Isolate & Concentrate | Grass-Fed Whey Concentrate | Whey Protein Isolate, Whey Protein Concentrate, Hydrolyzed Whey Protein | Collagen Peptides | Hydrolyzed Whey Protein Isolate |
| Flavor Options | 15 | 3 | 18 | 8 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 9 | 3 | 2 | Unflavored, plus 5 | 19 | 1 | 13 |
Best protein powder for muscle gain: Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate


Key product features
What you should know
Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate excels with its high protein content and clean, natural ingredients list, offering a gluten-free option that maximizes muscle protein synthesis without unnecessary additives.
- The peppermint hot chocolate flavor drew rave reviews from our product tester, who likened it to real peppermint hot chocolate without the typical sugar-laden toppings.
- While expensive at $2 per serving, this product delivers solid value due to its high protein content and high-quality ingredients.
- Transparent Labs Whey Protein Isolate is a well-rounded protein powder that delivers a high-quality 28 grams of protein per serving.
Best protein powder for weight loss: Sports Research Whey Protein Isolate


Key product features
What you should know
Sports Research Whey Protein Isolate offers 25 grams of protein in each serving, making it a great product for people who want to lose weight while supporting workout recovery.
- Our tester rated this formulation 4 out of 5 stars; it’s important to note that it’s sweetened with stevia, a sugar substitute.
- At $1.19 per serving, this protein powder falls in the middle of the road compared to other options on the market.
- This is a great choice for people who are watching their calorie intake or lose weight, containing only 150 calories per serving.
Best-tasting protein powder: Legion Whey+


Key product features
What you should know
Legion Whey+ sets itself apart with its commitment to natural ingredients and a wide array of unique, delightful flavors, avoiding artificial sweeteners, flavors, or dyes, and focusing on high-quality whey protein isolate to support muscle growth with minimal calorie intake.
- Our product tester reported that the cinnamon cereal flavor compared favorably to the well-known Cinnamon Toast Crunch cereal, leading to a taste score of 4.5 out of 5 stars.
- At $2 per serving, this whey protein powder is right on the median price point and slightly more than the average cost of $2.21 per serving for the protein powders featured here.
- With only 100 calories per serving, Legion Whey+ is an ideal solution if you’re looking for ways to boost your protein intake without eating into your caloric budget.
- One serving of Legion Whey+ includes 5.6 grams of BCAAs for muscle growth.
Best vanilla protein powder: Gainful Protein Powder


Key product features
What you should know
Gainful Protein Powder differentiates itself with its highly praised clean, natural formulation and innovative customization options, allowing users to tailor their protein blend to support weight loss goals based on lifestyle and diet preferences.
- You have ample flexibility to select the formula that fits your dietary needs and goals using the company’s customization feature.
- Gainful Protein Powder doesn’t rank highly from a value perspective due to the high cost per serving ($3.21) and the fact one bag contains just 14 servings.
- Despite its high price tag, this protein powder works well for vegans who want more control over what goes into their bodies.
- Although Gainful Protein Powder comes unflavored, you can select from nine “flavor boost” packets, including fan-favorite vanilla, to give it a specific taste.
Best pea protein powder: Nutricost Organic Pea Protein


Key product features
What you should know
Nutricost Organic Pea Protein contains 20 grams of protein and 30% of the daily value for iron, making it a great option for a plant-based protein powder.
- Nutricost Organic Pea Protein is a good option for those with an allergy or intolerance to dairy, soy, or egg, or for those following a vegan diet.
- This protein powder is very affordable compared to others on the market at only $0.47 to $0.65 per serving, depending on the size of the container.
- This product only comes in an unflavored option, but it will easily blend in with whichever beverage you’d like.
Best vegan protein powder: Ritual Daily Shake


Key product features
What you should know
Ritual Daily Shake is a high-quality plant-based protein powder that is Clean Label Project Certified and a Purity Award Product, which means it is free from pesticide residues, heavy metals, and plasticizers. The vanilla flavor is a fan favorite among reviewers.
- Ritual Daily Shake earned a perfect solubility score from our product tester.
- At $2.67 per serving and with only 15 servings per package, this plant-based protein powder doesn’t provide great bang for your buck compared to other options. But it may be worth the price knowing it minimizes your exposure to harmful chemicals.
- Ritual’s protein shake is made with pea protein, making it a good choice for vegetarians and vegans who want a plant-based supplement that supplies the nutrition they need to support their goals.
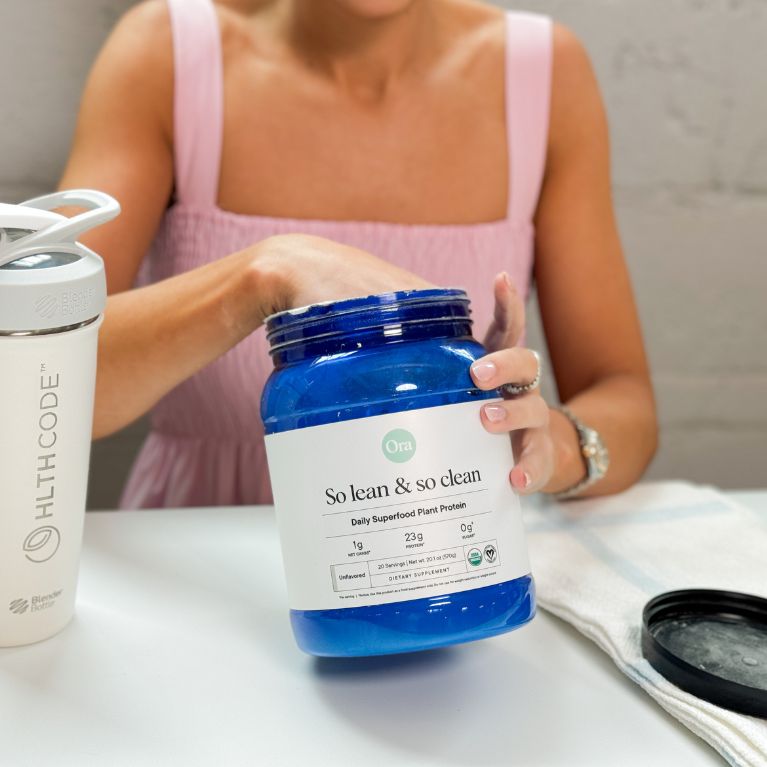
Best organic protein powder: Ora Organic So Lean & So Clean


Key product features
What you should know
With up to 23 grams of plant-based protein derived from USDA-certified organic ingredients, Ora Organic So Lean & So Clean is an ideal option for anyone seeking natural ingredients.
- One serving offers 22–23 grams of protein (depending on flavor) with hardly any carbs and fats, perfect as a pre- or post-workout plant-powered snack.
- Priced at around $2.50 per serving without a subscription, it’s more expensive than many options on our list. If you subscribe, you can save bout 15%, and each serving comes to
- According to reviewers, its rich vanilla flavor is enjoyable on its own, it also blends well with fruits and other mix-ins for a nutritious smoothie.
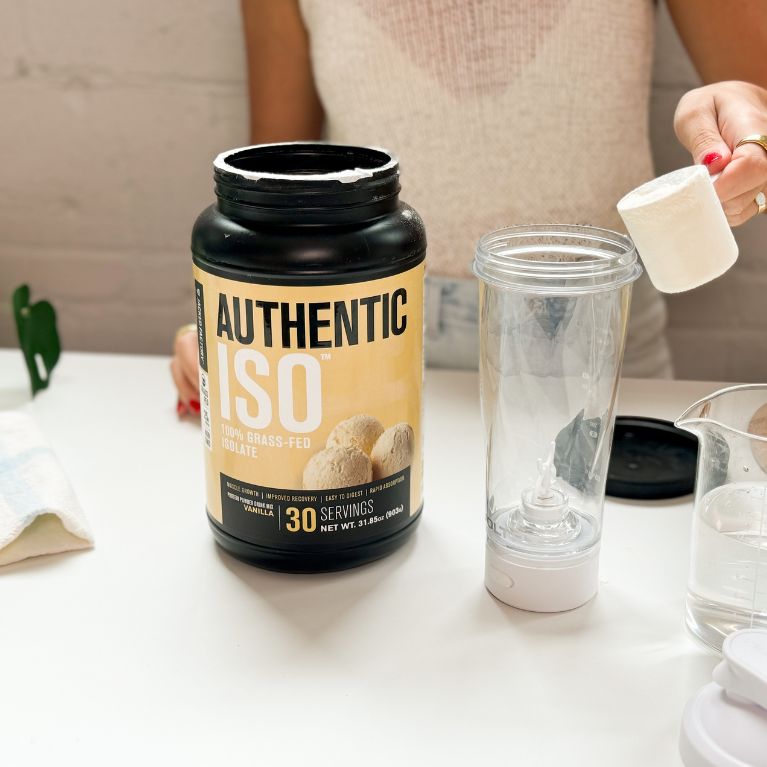
Best low-carb protein powder: Jacked Factory Authentic Iso


Key product features
What you should know
Jacked Factory Authentic Iso Vanilla is a high-quality whey protein protein powder with a rich vanilla taste designed to support muscle growth, recovery, and strength enhancement.
- Nearly all of the caloric content comes from protein, as one serving only contains one gram of carbs and 0.5 grams of fat.
- At $1.33 per serving, Jacked Factory Authentic Iso falls well below the average protein powder price.
- This a great choice for those who prefer a classic vanilla-flavored protein powder they can drink with or without mix-ins like fruit or nut butter.
- One scoop of Jacked Factory Authentic Iso contains only 100 calories, 25 grams of protein and 3 grams of carbs, ideal for those trying to lose weight.
Best protein powder for men: Kaged Protein Isolate Elite

Key product features
What you should know
Kaged Protein Isolate Elite uniquely blends fast-absorbing whey protein with slow-digesting micellar casein and milk protein isolates to provide a sustained release of amino acids for muscle repair and growth, totaling 25 grams of high-quality protein per serving.
- The combination of slow- and fast-digesting proteins promotes muscle growth and repair after a tough training session.
- At $1.88 per serving, Kaged Protein Isolate Elite falls right around the industry standard cost for protein powders.
- Male lifters and athletes who put their bodies through rigorous activities will appreciate how whey, casein, and milk protein isolate support optimal recovery.
Best cheap protein powder: Cellucor Cor-Performance Whey Isolate


Key product features
What you should know
Cellucor Cor-Performance protein features what the brand calls the Cor-Performance® Whey Protein Matrix, which includes both whey isolate and whey concentrate. However, based on the nutrition label, we cannot determine how much of each is present.
- Each serving of Cellucor Cor-Performance Whey delivers 24 grams of high-quality whey protein isolate, perfect for muscle recovery and supporting your fitness goals.
- At a price of around $1–$1.50 per serving, this is one of the most affordable options on the market, making it a top pick for budget-conscious shoppers.
- The low fat and carb content make it a great choice for those who want to increase their protein intake without adding unnecessary calories.
- Available in flavors molten chocolate and whipped vanilla, it mixes easily with water or milk, providing a smooth, clump-free texture.
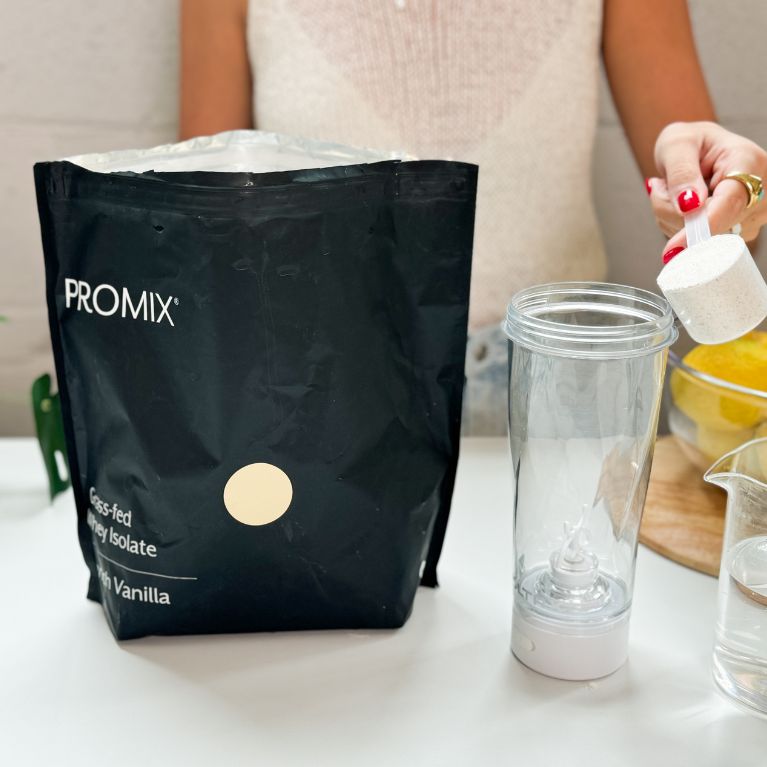
Best unflavored protein powder: Promix Unflavored Whey Protein


Key product features
What you should know
Promix Unflavored Whey Protein delivers 25 grams of grass-fed whey concentrate per serving, making it a high-quality option for muscle recovery and maintenance.
- Sourced from grass-fed cows, this whey protein may contain additional micronutrients like fatty acids, offering more than just a basic protein boost. (31) With only 1.5 grams of fat and 3 grams of carbs per serving, it’s ideal for those focused on increasing protein intake without added sugars or fillers.
- Priced at around $1.42 per serving for a 2-pound tub and $1.10 for a 5-pound tub, it falls into the mid-range price category, but offers a higher quality than many cheaper options due to its simple, additive-free ingredients.
- Promix Whey mixes smoothly with both water and milk, and customers praise its neutral taste, making it ideal for those who prefer flexibility in how they use their protein powder.
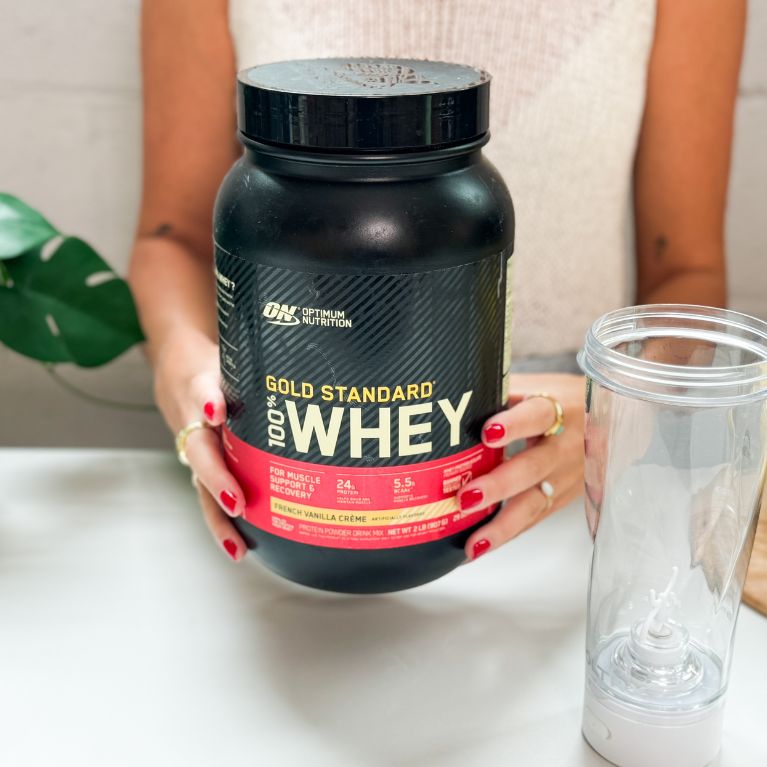
Best protein powder for women: Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey


Key product features
What you should know
Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey is an ideal choice for women who want to improve body composition, offering a blend of whey protein isolate, concentrate, and hydrolyzed whey for a rich amino acid profile and enhanced absorption.
- Although our testers rated the formulation 4.5 out of 5 stars, it’s important to note that some flavors contain artificial flavorings, colors, and sweeteners.
- Packed with 24 grams of protein per serving, Optimum Nutrition 100% Gold Standard Whey represents excellent value at an affordable price point of $1.61 per scoop.
- With more than 20 flavors to choose from, Optimum Nutrition’s whey protein powder is a good choice for women with discriminating palates.
Best collagen protein powder: Momentous Collagen Peptides


Key product features
What you should know
Momentous Collagen Peptides offer a potent blend of collagen types I and III, derived from grass-fed bovine, to support joint health, skin elasticity, and bone strength, addressing the natural decline in collagen production as we age.
- Our product tester rated the solubility 4 out of 5 stars, noting that it easily dissolved when given an extra stir.
- Although it doesn’t contain quite as much protein per serving as other supplements on this list, Momentous Collagen Peptides still comes in at an affordable price point of $1.73 per serving.
- Since collagen production slows with age, this unflavored supplement is especially beneficial for adults who want to maintain longevity and overall health.
- Momentous Collagen Peptides includes vitamin C and FORTIGEL to support collagen formation in the body.
Best chocolate protein powder: Dymatize ISO100


Key product features
What you should know
Dymatize ISO100 provides 25 grams of hydrolyzed whey protein isolate per serving, making it an excellent choice for muscle repair and recovery, especially post-workout.
- This protein powder stands out for its rich chocolate flavor, which delivers a smooth, indulgent taste without the excess carbs, sugars, or fats often found in flavored protein powders.
- Priced at around $1 per serving, it’s pretty affordable for a premium protein powder.
- At only 120 calories per serving, it’s a low-calorie option with a good amount of protein. Plus, with just 2 grams of carbs and 0.5 grams of fat per serving, it’s perfect for anyone on a low-carb or low-fat diet.
How we test protein powders
Finding the right supplement that meets health goals and delivers on promised claims requires time and research. On top of that, you need to consider product safety and price.
Dedicated to helping you find the best protein powder for muscle gain, we do the leg work for you. Our team tested, evaluated, and fact-checked dozens of protein powders on the market, taking many key factors into consideration, including effectiveness, quality, safety, and price, looking for supplements that rank high in several key areas to create our list of recommendations. Learn more about our whey protein powder scoring methodology and plant-based protein powder methodology here.
We used the following criteria to score each protein powder:
Testing criteria
Protein source—40%
The protein source is important because it affects the product’s digestibility, nutrient profile, and environmental impact. We consider the origin of the protein to ensure it meets vegan standards and provides a high-quality, sustainable option.
Here’s what we look for:
- Whey
- Casein
- Soy
- Pea
- Brown rice
- Hemp
- Lentil
- Chia
- Pumpkin Seed
- Blend
Complete protein—20%
Whether the protein is complete is crucial for determining if it provides all nine essential amino acids needed for muscle repair and overall health. We consider this to ensure that the product can serve as a reliable, sole protein source without requiring additional supplementation.
Macronutrient calories per serving—15%
The balance of macronutrients per serving is important for managing energy levels, weight, and overall nutrition. We consider these calories to evaluate if the product supports specific dietary goals, such as high-protein or low-carb diets.
Our factors in this rating include:
- Calories from protein
- Calories from carbs
- Calories from fats
Total protein per serving—15%
The amount of protein per serving is a key factor in determining the product’s effectiveness in meeting daily protein needs.
Our factors in this rating include:
- 20 grams of protein or less per serving
- 21 to 30 grams of protein per serving
- Over 30 grams of protein per serving
Price per gram of protein—5%
Understanding the cost efficiency is important for those who want to manage their budget while meeting their nutritional needs. We consider the price per gram of protein to compare the value of different products.
These are the ranges we consider:
- $0.30 to $0.50 per gram
- $0.60 to $0.80 per gram
- $0.90+ per gram
Sweeteners—5%
Sweeteners play a significant role in the taste, caloric content, and health impact of the product. We consider the type and amount of sweeteners used to evaluate their impact on flavor, their suitability for low-sugar diets, and any potential health implications.
Here are the common ones we evaluate:
- Sugar
- Dextrose
- Honey, agave
- Stevia
- Maltodextrin
- Erythritol
- Monk fruit
- Sucralose
- Aspartame
- Xylitol, acesulfame
About our chemical lab analysis
Our dedicated team of product testers have hands-on experience using the protein powders we evaluate. In this article, we incorporate their insightful feedback, including both the positive and less favorable aspects of each supplement. However, our commitment to transparency doesn’t end there.
To guarantee the products we recommend are from credible and reputable brands adhering to industry-standard best practices for quality and safety, we took the extra step of subjecting them to third-party testing by Ellipse Analytics. Many of the products underwent thorough analysis for safety, purity, and ingredient accuracy. The testing confirms the accuracy of ingredient amounts and ensures the absence of harmful levels of contaminants, pesticides, heavy metals, bisphenols, and phthalates.
The results of these assessments are incorporated into the individual reviews.
What is Protein Powder?
Protein powder is a nutritional supplement that’s protein-rich, containing at least 10 grams of protein per serving, typically 20 grams per serving or more. The protein is often sourced from whey, casein, collagen, or plant-based sources such as yellow split peas, rice, and more. Many protein powders are flavored either naturally or artificially, though some are unflavored. Protein powder is designed to be added to a liquid beverage, such as water or milk, but may also be suitable for baking. Carbohydrate and fat content can widely vary by product.
Benefits of Protein Powder
Protein is an essential nutrient that supports a variety of important bodily functions such as muscle maintenance and growth, cell repair, and overall health. (1) Most people get all the protein they need from food. (3)
However, people with higher protein needs—like bodybuilders, athletes, and older adults—may have a harder time getting enough protein from food to meet needs and support goals. (3, 17) Protein powder is a convenient and easy way to add protein to the diet. You can blend it into a shake, mix it with yogurt, or add it to pancake batter.
Some of the benefits of protein powder include:
- Maintaining muscle mass during weight loss (40)
- Supporting muscle recovery after an intense workout (3)
- Building muscle following resistance training (3)
- Preventing age-related muscle loss (17)
Supplementing with whey protein may even improve blood pressure, according to a recent review study of randomized controlled trials published in Nutrition, Metabolism, and Cardiovascular Diseases. (50) However, more research is needed to better understand the connection between whey protein and blood pressure and the right dose to get the benefit. (50)
How to Use Protein Powder
Protein powder is typically mixed with water or another liquid beverage. Be sure to follow the instructions of whichever product you choose, since serving sizes vary. Many protein powders come with a scoop to make it easy to measure out servings. Simply blend the appropriate serving of protein powder into your beverage of choice. Blending protein powder can be easily done in a blender bottle or electric blender.
Potential Side Effects of Protein Powder
Side effects of protein powder can vary by person. Some people are lactose intolerant or sensitive, and may experience digestive discomfort or bloating from consuming a whey-based protein powder. Those with dietary allergies or sensitivities should check the nutrition label before purchasing a protein powder. It’s best to purchase a protein powder from a reputable brand, such as those listed above. As always, you may consult with your doctor, a certified nutritionist, or a registered dietician before adding a nutritional supplement like protein powder to your diet.
Who should take protein powder?
Anyone unable to get the protein they need from food alone may benefit from taking protein powder. Athletes and bodybuilders often use protein powder to meet higher protein needs to maintain or build muscle. (3)
But protein powder isn’t just for athletes. Anyone unable to meet protein needs from food alone may need to take protein powder, like those following a reduced-calorie diet for weight loss, older adults with a poor appetite, or weight-loss surgery patients with protein deficiency.
Research shows that higher protein diets may support weight loss by enhancing body composition (helping you lose fat and retain muscle), controlling hunger, and increasing metabolism. (39) Protein powder may help people trying to lose weight get the extra protein they need in a convenient and easy to use form.
When supplementing with protein powder for weight loss, you need to include it as part of your balanced eating plan. Adding a protein supplement without modifying your usual intake may increase calorie intake, leading to weight gain.
Older adults may also benefit from taking protein powder when they’re unable to meet their higher protein needs due to changes in appetite. (40) A decrease in appetite and food intake is normal as you get older, but often leads to weight loss and an excessive loss of muscle mass (sarcopenia) that affects strength and mobility. (40, (17) Adding protein powder to hot cereal, soup, or casseroles is an easy way for older adults to get more protein without affecting appetite.
People who had weight loss surgery may also take protein powder. Protein deficiency is a complication of weight loss surgery, causing hair loss, muscle loss, and poor wound healing. (41) Protein and protein quality are important, and foods high in leucine are encouraged following weight loss surgery. (41) For those unable to meet protein needs from food, a protein powder rich in leucine, like whey or pea, may reduce risk of deficiency. (42)
What ingredients to look for in protein powder
Since the goal is to get more protein, you want a supplement with protein as the main ingredient. Protein powders may contain other ingredients you may want and some you don’t.Check the nutrition label and ingredients list to find the information you need.
Protein
You want a powder that lists a protein as the first ingredient, such as whey, casein, pea, soy, or egg. These proteins provide all of the essential amino acids your body needs. (1) Choose the protein that best aligns with your personal preferences, diet needs, and health goals.
Other active ingredients
Protein is the main active ingredient in all protein powders, but some may contain other ingredients, such as creatine, branch-chain amino acids (BCAA), probiotics, fiber, digestive enzymes, or MCT oil.
Some of the added ingredients may support your goals, like creatine for exercise performance and fiber to support regular bowel movements. ( (18, 43) But some may cause side effects, like abdominal pain with MCT oil. (43)
You want to pay close attention to the other active ingredients listed on the label to make sure you’re getting what you want and need. Talk to your doctor or consult with a registered dietitian for personalized guidance.
Sweeteners
Protein powders may use sweeteners to improve flavor, including sugar and nonnutritive sweeteners. You want a protein powder that has little to no added sugar so you don’t consume any unnecessary calories that offer no health benefits. (44)
Nonnutritive sweeteners keep protein powders sugar free, but may include artificial sweeteners like sucralose or acesulfame potassium. Though artificial sweeteners are generally recognized as safe, it’s always best to limit intake of artificial ingredients. (16) Natural sugar-free sweeteners like stevia or monk fruit are better options, but they can have a bitter aftertaste.
Try to avoid protein powders with added fillers, preservatives, and artificial flavors and colors.
How much protein powder should I take?
The amount of protein powder to take depends on needs, goals, and usual diet. Protein powder is a supplement and shouldn’t replace real food.
Though there’s no set number for how much protein powder to take, using the supplement once or twice a day—1-2 servings—may provide the extra protein you need to reach your goals.
The ISSN says to maintain and build muscle, you need 20-40 grams of protein every three to four hours. (3) Protein powder is a convenient way to get the necessary protein when you can’t eat a high-protein meal or snack.
You may also take protein powder after a workout when you don’t have the appetite to eat, so you get the amino acids necessary for muscle-building. (3) Though, current research suggests that you no longer need to consume protein immediately after a workout to support muscle recovery. (3) Your muscles remain sensitive to protein for up to 24 hours after a workout and any protein-rich meal you eat within that period boosts muscle protein synthesis. (3)
Other protein powders we tried
While researching the best protein powders on the market, we tried over 100, so not all could make the cut. Here are some products we liked but that didn’t make our list.
- Transparent Labs Mass Gainer: While we liked the taste of this formula and found it to have good solubility, the high calorie count (750 per serving) makes this protein powder hard to recommend for all individuals. Instead, this one is best suited for those with goals of big gains or those who are trying to gain weight.
- Naked Goat: This protein powder is made with a unique source—goat whey. However, our testers found that upon mixing the protein, it was pretty foamy and the unflavored version had a gritty, slightly unpleasant taste.
- Momentous Protein Powder: Our tester found this protein powder difficult to mix, and that clumps were left behind. Additionally, at $2.50 per serving with 20 grams of protein per serving, this supplement is higher cost with slightly lower protein content than many options on our list.
FAQs
Should I take protein powder every day?
Whether you should use protein powder every day depends on several factors, including diet, age, activity level, and fitness goals. Aging adults and athletes wanting to build muscle have higher protein needs and may benefit from a daily protein supplement to help meet their daily intake needs. Taking daily protein powder is unnecessary if you already eat plenty of protein through food.
When is the best time of day to take protein powder?
It’s essential to prioritize overall daily protein intake rather than focusing solely on the timing of your protein powder intake. That said, one of the best times to take protein powder is post-workout to support muscle recovery and development of size and/or performance, depending on how you exercise. It’s also important to consume adequate protein with breakfast, to ensure a positive muscle protein balance after sleep, between meals to manage hunger, and before bedtime to support muscle recovery throughout the night.
Is protein powder good for you?
A good protein powder can be a helpful supplement to boost protein intake for those with elevated protein needs. It may be good for you if you struggle to eat enough protein through food alone and benefit from the convenience of a supplement. However, protein powder should not replace a balanced diet, including a variety of whole foods.
How much protein should you eat per day?
Most Americans meet the recommended dietary allowance (RDA) for protein of 0.8 grams per kilogram daily. (37) However, physically active adults have greater protein needs. According to the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics, athletes need 1.2 to 2 grams of protein per kilogram daily. (38) For these individuals, consuming enough protein through food alone can be challenging, and protein powder may come in handy.
These statements have not been evaluated by the Food and Drug Administration. These products are not intended to diagnose, treat, cure, or prevent any diseases.
Our experts
Robert Wildman, Phd, RD, LD, CISSN, FISSN
Dr Robert Wildman (“Dr Rob”) is a globally renowned exercise, fitness, and nutrition expert who speaks around the world on exercise and sport nutrition, and continues to work with professional and elite athletes to achieve their highest level of performance as well as health and fitness. Rob received his PhD from The Ohio State University, earned his MS from Florida State University, and earned his BS from the University of Pittsburgh. He is also a registered and licensed dietitian.
Amanda Dvorak, CPT
Amanda Dvorak has been writing fitness and nutrition content for over three years. She played softball throughout her childhood and started doing CrossFit in 2015. While she still enjoys doing CrossFit workouts in her garage gym, she also loves lifting heavy weights, running, and hiking. Amanda is currently studying to become a certified personal trainer through the International Sports Sciences Association (ISSA).
Jessica Coulon
Jessica Coulon is a writer and editor who specializes in fitness, health, nutrition, and science content. Previously, she was an editor for Popular Mechanics and Bicycling, where she covered pro cycling news, wrote how-to guides, and tested all the latest and greatest bike gear. She was also a regular shoe tester and contributor for Runner’s World. You can often find her skiing or riding her mountain bike, and racing with the F1RE female enduro team.
Kelly Uhler
Kelly has a multifaceted background in elder care, health care, and copywriting. She has worked for organizations such as A Place For Mom and Homecare.com, which gave her the opportunity to work closely with families, providing reliable information to help them make informed decisions about their loved one’s health, safety, and quality of life.

Perry Nix
MS, RD, LD
About Author
Perry Nix, MS, RD, LD, is a registered dietitian and freelance nutrition writer who resides in Texas with her two rambunctious boys and firefighter husband. She earned her degrees from Texas Tech University and has since gained experience in public health, corporate wellness, and clinical settings. Today, she enjoys writing about sports nutrition and teaching others how to properly fuel for an active, adventurous, and balanced lifestyle.
References
- Harvard School of Public Health. Protein. Accessed December 30, 2023.
- Kerstetter JE, Kenny AM, Insogna KL. Dietary protein and skeletal health: a review of recent human research. Curr Opin Lipidol. 2011;22(1):16-20. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4659357/
- Jäger R, Kerksick CM, Campbell BI, et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2017;14:20. Published 2017 Jun 20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-017-0177-8
- Leidy HJ, Clifton PM, Astrup A, Wycherley TP, Westerterp-Plantenga MS, Luscombe-Marsh ND, Woods SC, Mattes RD. The role of protein in weight loss and maintenance. Am J Clin Nutr. 2015 Jun;101(6):1320S-1329S. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.084038. Epub 2015 Apr 29. PMID: 25926512. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25926512/#:~:text=Collectively%2C%20these%20data%20suggest%20that,or%20all%20of%20these%20health
- Moon, J.M., Ratliff, K.M., Blumkaitis, J.C, Harty, P.S, Zabriskie, H.A, Stecker, R.A., Currier, B.S., Jagim, A.R., Jäger, R., Purpura, M., & Kerksick CM. (2020, December 1). Effects of daily 24-gram doses of rice or whey protein on resistance training adaptations in trained males. J Int Soc Sports Nutr, 17(1):60. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7706190/
- Madureira AR, Pereira CL., Gomes AMP, Pintado ME, Xavier Malcata F. Bovine whey proteins – Overview on their main biological properties. Food Res Int. 2007;40(10):1197-1211. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7126817/
- Moon, J., & Koh, G. (2020). Clinical Evidence and Mechanisms of High-Protein Diet-Induced Weight Loss. Journal of obesity & metabolic syndrome, 29(3), 166–173.https://doi.org/10.7570/jomes20028
- Nutrition and Athletic Performance. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 41(3):p 709-731, March 2009. | http://DOI: 10.1249/MSS.0b013e31890eb86
- Chen IJ, Liu CY, Chiu JP, Hsu CH. Therapeutic effect of high-dose green tea extract on weight reduction: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Nutr. 2016;35(3):592-599.
- Science Direct. (n.d.). Pea Protein. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/agricultural-and-biological-sciences/pea-protein
- Guillin FM, Gaudichon C, Guérin-Deremaux L, Lefranc-Millot C, Airinei G, Khodorova N, Benamouzig R, Pomport PH, Martin J, Calvez J. Real ileal amino acid digestibility of pea protein compared to casein in healthy humans: a randomized trial. Am J Clin Nutr. 2022 Feb 9;115(2):353-363. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqab354. PMID: 34665230.
- Lopez MJ, Mohiuddin SS. Biochemistry, Essential Amino Acids. [Updated 2023 Mar 13]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK557845/
- Martínez Y, Li X, Liu G, Bin P, Yan W, Más D, Valdivié M, Hu CA, Ren W, Yin Y. The role of methionine on metabolism, oxidative stress, and diseases. Amino Acids. 2017 Dec;49(12):2091-2098. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-017-2494-2. Epub 2017 Sep 19. PMID: 28929442.
- Martinho DV, Nobari H, Faria A, Field A, Duarte D, Sarmento H. Oral Branched-Chain Amino Acids Supplementation in Athletes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients. 2022; 14(19):4002. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194002
- Clean Label Project. Purity Award. Accessed August 26, 2024. https://cleanlabelproject.org/purity-award/
- Barber TM, Kabisch S, Pfeiffer AFH, Weickert MO. The Health Benefits of Dietary Fibre. Nutrients. 2020 Oct 21;12(10):3209. https:/doi.org/10.3390/nu12103209. PMID: 33096647; PMCID: PMC7589116.
- Teixeira FJ, Matias CN, Faleiro J, Giro R, Pires J, Figueiredo H, Carvalhinho R, Monteiro CP, Reis JF, Valamatos MJ, Teixeira VH, Schoenfeld BJ. A Novel Plant-Based Protein Has Similar Effects Compared to Whey Protein on Body Composition, Strength, Power, and Aerobic Performance in Professional and Semi-Professional Futsal Players. Front Nutr. 2022 Jul 19;9:934438. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2022.934438. PMID: 35938106; PMCID: PMC9355667. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9355667/#:~:text=Several%20research%20studies%20have%20compared,soy%20(31%2C%2032)
- Neville CE, Young IS, Gilchrist SE, McKinley MC, Gibson A, Edgar JD, Woodside JV. Effect of increased fruit and vegetable consumption on physical function and muscle strength in older adults. Age (Dordr). 2013 Dec;35(6):2409-22. doi: 10.1007/s11357-013-9530-2. Epub 2013 Apr 2. PMID: 23543264; PMCID: PMC3825010. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3825010/
- Patricia JJ, Dhamoon AS. Physiology, Digestion. [Updated 2022 Sep 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2024 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK544242/
- Cava E, Padua E, Campaci D, Bernardi M, Muthanna FMS, Caprio M, Lombardo M. Investigating the Health Implications of Whey Protein Consumption: A Narrative Review of Risks, Adverse Effects, and Associated Health Issues. Healthcare (Basel). 2024 Jan 18;12(2):246. doi: 10.3390/healthcare12020246. PMID: 38255133; PMCID: PMC10815430. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10815430/
- Mitchell WK, Wilkinson DJ, Phillips BE, Lund JN, Smith K, Atherton PJ. Human Skeletal Muscle Protein Metabolism Responses to Amino Acid Nutrition. Adv Nutr. 2016 Jul 15;7(4):828S-38S. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.115.011650. PMID: 27422520; PMCID: PMC4942869.
- Magnuson BA, Roberts A, Nestmann ER. Critical review of the current literature on the safety of sucralose. Food Chem Toxicol. 2017;106(Pt A):324-355. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2017.05.047
- Schoenfeld BJ, Aragon AA. How much protein can the body use in a single meal for muscle-building? Implications for daily protein distribution. J Int Soc Sports Nutr. 2018 Feb 27;15:10. https:/doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0215-1. PMID: 29497353; PMCID: PMC5828430.
- Kim J. Pre-sleep casein protein ingestion: new paradigm in post-exercise recovery nutrition. Phys Act Nutr. 2020 Jun 30;24(2):6-10. https://doi.org/10.20463/pan.2020.0009. PMID: 32698256; PMCID: PMC7451833.
- Ohnuma, T., Toda, A., Kimoto, A., Takebayashi, Y., Higashiyama, R., Tagata, Y., Ito, M., Ota, T., Shibata, N., & Arai, H. (2016). Benefits of use, and tolerance of, medium-chain triglyceride medical food in the management of Japanese patients with Alzheimer’s disease: a prospective, open-label pilot study. Clinical interventions in aging, 11, 29–36. https://doi.org/10.2147/CIA.S95362
- Jäger, R., Kerksick, C.M., Campbell, B.I. et al. International Society of Sports Nutrition Position Stand: protein and exercise. J Int Soc Sports Nutr 14, 20 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-017-0177-8
- Wolfe RR. Update on protein intake: importance of milk proteins for health status of the elderly. Nutr Rev. 2015 Aug;73 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):41-7. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv021. PMID: 26175489; PMCID: PMC4597363. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4597363/
- Atanu Jana, Chapter 8 – High protein dairy foods: technological considerations, Editor(s): Adriano Gomes da Cruz, C. Senaka Ranadheera, Filomena Nazzaro, Amir Mohammad Mortazavian, Dairy Foods, Woodhead Publishing, 2022, Pages 159-193, https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/B9780128204788000134?via%3Dihub#preview-section-cited-by
- Wolfe RR. Update on protein intake: importance of milk proteins for health status of the elderly. Nutr Rev. 2015 Aug;73 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):41-7. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv021. PMID: 26175489; PMCID: PMC4597363. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4597363/
- Ianiro G, Pecere S, Giorgio V, Gasbarrini A, Cammarota G. Digestive Enzyme Supplementation in Gastrointestinal Diseases. Curr Drug Metab. 2016;17(2):187-93. doi: 10.2174/138920021702160114150137. PMID: 26806042; PMCID: PMC4923703. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26806042/
- AMark Timlin, Ellen Fitzpatrick, Kieran McCarthy, John T. Tobin, Eoin G. Murphy, Karina M. Pierce, John P. Murphy, Deirdre Hennessy, Michael O’Donovan, Niamh Harbourne, André Brodkorb, Tom F. O’Callaghan, Impact of varying levels of pasture allowance on the nutritional quality and functionality of milk throughout lactation, Journal of Dairy Science, Volume 106, Issue 10, 2023, Pages 6597-6622, ISSN 0022-0302, https://doi.org/10.3168/jds.2022-22921.
- Jang H, Park K. Omega-3 and omega-6 polyunsaturated fatty acids and metabolic syndrome: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Nutr. 2020 Mar;39(3):765-773. doi: 10.1016/j.clnu.2019.03.032. Epub 2019 Apr 5. PMID: 31010701. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31010701/
- Robinson LE, Mazurak VC. N-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids: relationship to inflammation in healthy adults and adults exhibiting features of metabolic syndrome. Lipids. 2013 Apr;48(4):319-32. doi: 10.1007/s11745-013-3774-6. Epub 2013 Mar 1. PMID: 23456976. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23456976/
- De Siena M, Raoul P, Costantini L, Scarpellini E, Cintoni M, Gasbarrini A, Rinninella E, Mele MC. Food Emulsifiers and Metabolic Syndrome: The Role of the Gut Microbiota. Foods. 2022 Jul 25;11(15):2205. doi: 10.3390/foods11152205. PMID: 35892789; PMCID: PMC9331555. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9331555/
- Robert E Bergia, Joshua L Hudson, Wayne W Campbell, Effect of whey protein supplementation on body composition changes in women: a systematic review and meta-analysis, Nutrition Reviews, Volume 76, Issue 7, July 2018, Pages 539–551, https://doi.org/10.1093/nutrit/nuy017
- Kuo, Y. Y., Chang, H. Y., Huang, Y. C., & Liu, C. W. (2022). Effect of Whey Protein Supplementation in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Nutrients, 14(19), 4210. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu14194210
- Oikawa, S. Y., Kamal, M. J., Webb, E. K., McGlory, C., Baker, S. K., & Phillips, S. M. (2020). Whey protein but not collagen peptides stimulate acute and longer-term muscle protein synthesis with and without resistance exercise in healthy older women: a randomized controlled trial. The American journal of clinical nutrition, 111(3), 708–718. https://doi.org/10.1093/ajcn/nqz332
- Hofman DL, van Buul VJ, Brouns FJ. Nutrition, Health, and Regulatory Aspects of Digestible Maltodextrins. Crit Rev Food Sci Nutr. 2016 Sep 9;56(12):2091-100. https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2014.940415. PMID: 25674937; PMCID: PMC4940893.
- Cleveland Clinic. Collagen. Updated May 23, 2022. Accessed December 29, 2023. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/articles/23089-collagen
- Shenoy M, Abdul NS, Qamar Z, Bahri BMA, Al Ghalayini KZK, Kakti A. Collagen Structure, Synthesis, and Its Applications: A Systematic Review. Cureus. 2022;14(5):e24856. Published 2022 May 9. http://doi:10.7759/cureus.24856
- Khatri M, Naughton RJ, Clifford T, Harper LD, Corr L. The effects of collagen peptide supplementation on body composition, collagen synthesis, and recovery from joint injury and exercise: a systematic review. Amino Acids. 2021;53(10):1493-1506. http://doi:10.1007/s00726-021-03072-x
- de Miranda RB, Weimer P, Rossi RC. Effects of hydrolyzed collagen supplementation on skin aging: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Int J Dermatol. 2021;60(12):1449-1461. http://doi:10.1111/ijd.15518
- Zdzieblik D, Oesser S, König D. Specific Bioactive Collagen Peptides in Osteopenia and Osteoporosis: Long-Term Observation in Postmenopausal Women. J Bone Metab. 2021;28(3):207-213. http://doi:10.11005/jbm.2021.28.3.207
- DePhillipo NN, Aman ZS, Kennedy MI, Begley JP, Moatshe G, LaPrade RF. Efficacy of Vitamin C Supplementation on Collagen Synthesis and Oxidative Stress After Musculoskeletal Injuries: A Systematic Review. Orthop J Sports Med. 2018;6(10):2325967118804544. Published 2018 Oct 25. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30386805/
- Potier M, Tomé D. Comparison of digestibility and quality of intact proteins with their respective hydrolysates. J AOAC Int. 2008 Jul-Aug;91(4):1002-5. PMID: 18727562. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/18727562/
- Khemtong C, Kuo CH, Chen CY, Jaime SJ, Condello G. Does Branched-Chain Amino Acids (BCAAs) Supplementation Attenuate Muscle Damage Markers and Soreness after Resistance Exercise in Trained Males? A Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Nutrients. 2021 May 31;13(6):1880. doi: 10.3390/nu13061880. PMID: 34072718; PMCID: PMC8230327.
- Volpi E, Nazemi R, Fujita S. Muscle tissue changes with aging. Curr Opin Clin Nutr Metab Care. 2004 Jul;7(4):405-10. https:/doi.org/10.1097/01.mco.0000134362.76653.b2. PMID: 15192443; PMCID: PMC2804956.
- Vajdi, M., Musazadeh, V., Zareei, M., Adeli, S., Karimi, A., Hojjati, A., Darzi, M., Shoorei, H., & Abbasalizad Farhangi, M. (2023). The effects of whey protein on blood pressure: A systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nutrition, metabolism, and cardiovascular diseases : NMCD, 33(9), 1633–1646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.numecd.2023.05.025
- Chapman, I., Oberoi, A., Giezenaar, C., & Soenen, S. (2021). Rational Use of Protein Supplements in the Elderly-Relevance of Gastrointestinal Mechanisms. Nutrients, 13(4), 1227. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13041227
- Sherf Dagan, S., Goldenshluger, A., Globus, I., Schweiger, C., Kessler, Y., Kowen Sandbank, G., Ben-Porat, T., & Sinai, T. (2017). Nutritional Recommendations for Adult Bariatric Surgery Patients: Clinical Practice. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.), 8(2), 382–394. https://doi.org/10.3945/an.116.014258
- Slywitch E, Savalli C, Duarte ACG, Escrivão MAMS. Iron Deficiency in Vegetarian and Omnivorous Individuals: Analysis of 1340 Individuals. Nutrients. 2021; 13(9):2964. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu13092964
- Kerksick, C. M., Wilborn, C. D., Roberts, M. D., Smith-Ryan, A., Kleiner, S. M., Jäger, R., Collins, R., Cooke, M., Davis, J. N., Galvan, E., Greenwood, M., Lowery, L. M., Wildman, R., Antonio, J., & Kreider, R. B. (2018). ISSN exercise & sports nutrition review update: research & recommendations. Journal of the International Society of Sports Nutrition, 15(1), 38. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12970-018-0242-y
- American Heart Association. Added sugars. Accessed July 6, 2024. https://www.heart.org/en/healthy-living/healthy-eating/eat-smart/sugar/added-sugars
- Snetselaar LG, de Jesus JM, DeSilva DM, Stoody EE. Dietary Guidelines for Americans, 2020-2025: Understanding the Scientific Process, Guidelines, and Key Recommendations. Nutr Today. 2021;56(6):287-295. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34987271/
- Carbone JW, Pasiakos SM. Dietary Protein and Muscle Mass: Translating Science to Application and Health Benefit. Nutrients. 2019;11(5):1136. Published 2019 May 22. http:doi:10.3390/nu1105113